Desktop Virtualization
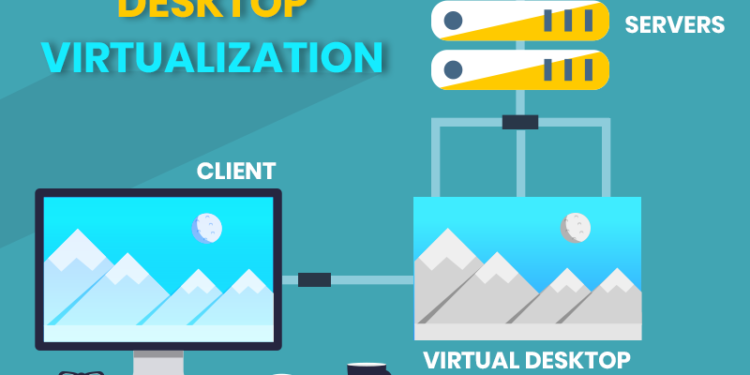
Desktop virtualization is a software technology that separates a desktop environment from the associated application software and physical client device. The technology can be used in a variety of ways, including extending the capabilities of a single machine to host a large number of virtual machines. There are a number of benefits of desktop virtualization, including ease of deployment and reduced costs. Read on for more information about desktop virtualization. Also, learn about the different types of desktop virtualization available, including hostbased desktop virtualization.
Disadvantages of desktop virtualization
Although Desktop Virtualization can improve the computing experience of users, it has disadvantages as well. Users are not able to call the same Operating System and applications as others. Administrators can limit the amount of server resources that each user can use. Some companies offer Desktop Virtualization services as a cloud-based service, which means that users can pay a monthly fee to use them. However, desktop virtualization requires a capital investment in hardware and software.
Desktop virtualization requires powerful servers and large amounts of bandwidth for data transfer. It also places heavy demands on storage and network bandwidth. Nevertheless, its advantages are significant. This technology can simplify network management, bandwidth throttling, and quality of service. Moreover, thin clients can significantly reduce acquisition costs. Although it does have many benefits, desktop virtualization is not suitable for all types of infrastructures. It’s best suited for homogeneous infrastructures.
Desktop applications aren’t as flexible and user-friendly as web apps. The user interface is more difficult to customize, which isn’t ideal for the most demanding users. However, the advantage of desktop virtualization is that users don’t have to deal with the technicalities of installing and managing virtual machines. They can even run multiple operating systems, such as Windows, on the same machine. And because they are hosted on the same machine, desktop virtualization also reduces the risk of a security breach.
Another disadvantage of desktop virtualization is its cost. Compared to virtual machines, desktop virtualization is incredibly expensive. And the downsides are outweighed by its advantages. Despite these limitations, desktop virtualizations is a great option for enterprise IT. Most businesses use desktop virtualization for their computers, but it can be difficult to transition the entire system from a traditional desktop environment to a modern, cloud-based one.
Desktop virtualization is an excellent solution for businesses that are struggling with the costs of maintaining individual workstations. But, it is not without its disadvantages. Before implementing this technology, organizations need to consider their goals for desktop virtualizations. Some common goals are cost reduction, improved system administration, user flexibility, and keeping up with trends and competition. But before implementing this technology, it is important to evaluate its advantages and drawbacks.
Compatibility
Desktop virtualization is a type of computer management technology that allows a business to run its entire desktop in a networked container. The technology allows businesses to use different versions of Windows on different computers, and it can improve application resource usage by using local system resources. However, the technology does not always allow applications developed for one architecture to run on another. In some cases, it can run Windows 7 on top of Apple’s OS X, but it is not yet possible to use the same version of Windows on a Mac.
One of the primary challenges associated with Desktop Virtualization is maintaining optimal bandwidth. Because this technology requires additional bandwidth, your network infrastructure must support it. This means that your WAN lines must have adequate bandwidth to accommodate the DV users that are scattered around. If your network is not up to the task, insufficient bandwidth may affect the quality of the display. This is especially true when streaming applications from the server. Desktop Virtualizations is available in three types.
This type of technology works by abstracting the desktop environment from the physical computer and providing access to the virtualized desktop from any location. It is possible to access the virtualized desktop from any computer with an internet connection. The user will not be aware of any difference in their working experience. It is because they are accessing a window in a virtualized environment that exists on a centralized server at a remote data center.
Although desktop virtualization is widely adopted by business owners, the technology has not been widely adopted by the general public yet. Although it is widely used, the term “VDI” is often incorrectly applied to any desktop virtualizations implementation. Compatibility of desktop virtualizations with different platforms is important because this type of technology requires varying levels of desktop customization. The key to desktop virtualizations success is that it allows for a large degree of customization.
The use of desktop virtualization is increasing, especially because of the widespread use of remote workstations. Desktop virtualizations allows for easy access to office applications and data from remote locations, enabling companies to better accommodate geographically dispersed workers. Aside from providing better security, desktop virtualizations also enables organizations to make better use of the cloud. There are some security risks with desktop virtualizations. For example, users could run malicious software that compromises the integrity of a computer.
Cost
The initial cost of desktop virtualization is higher than traditional infrastructure solutions. But with local storage, the costs are drastically reduced – in some cases, by as much as 50%. Desktop virtualizations enables enterprises to leverage existing infrastructure while minimizing the cost of server and storage. The cost savings, however, are temporary. The cost of desktop virtualizations is now within reach of a broader group of organizations. It helps companies deliver the same level of productivity and security without the need to purchase expensive desktops.
For example, Citrix VDI-in-a-Box costs $1,950 for a pack of ten desktops. This includes the first year of support. But licenses cost around $160 apiece. And the total cost of VDI software will probably run into the hundreds of thousands of dollars. As such, the total cost of desktop virtualization may be higher than it is worth. But the benefits of remote work are worth it.
CIOs and IT managers have a significant advantage over traditional desktop infrastructure when it comes to desktop virtualization. These systems allow IT departments to transform their business without sacrificing employee productivity or security. While the ROI is low, the initial investment may not be enough to attract a
larger pool of users. To offset the costs, CIOs should consider the long-term costs of desktop virtualization. Many organizations can save more than 50% or more on server licenses, and they can also reduce operating costs by reducing maintenance and administration.
The cost of desktop virtualization varies by industry. The average enterprise costs around $25,000 for desktop virtualizations. This includes the cost of the hardware, operating system, applications, and thin-clients. Thin-clients are more expensive than individual desktops. Furthermore, DV requires additional bandwidth, which can be expensive. And it may also be difficult to maintain network infrastructure if the DV users don’t access the network frequently.
The cost of VDI varies greatly, as storage configurations are not consistent across solutions. Furthermore, VDI also requires a dedicated IT staff for support and management, which may add to the total cost of ownership. But the benefits are worth the expense. The benefits of VDI are more widespread than you think. If you want to adopt it, consider a few important considerations. So, when comparing desktop virtualization solutions, don’t just choose the first one that looks good.
Host-based desktop virtualization
Desktop virtualization is a technology that allows users to view and interact with a virtual desktop over a network. It uses remote display protocols on client devices such as traditional PCs, thin clients, or zero clients. A user can use a persistent desktop or a new nonpersistent one with every login, depending on his or her preferences. Host-based desktop virtualization is a great solution for organizations that need to provide remote access to all their users.
A host-based desktop virtualization solution provides a secure environment for users to access their desktop from any location. This feature can be used in conjunction with other technologies, such as application virtualization, and user profile management systems. It also supports a full disaster recovery strategy. The technology automatically backs up all components in a data center and traditional redundant maintenance systems. The resulting recovery process is simple and quick, even if the physical device of the user is destroyed.
Desktop virtualization can help IT departments make the best use of their hardware investments and minimize the amount of computing needed at the end-user level. By centrally managing desktop deployment, desktop virtualizations makes it possible for IT to provide more flexibility to end users. Two primary deployment models are virtual machine-based and session-based. With desktop virtualizations, users can securely access the corporate desktop from a thin client, tablet, or home.
Host-based desktop virtualization is a popular type of desktop virtualizations. It uses host-based virtual machines to provide both persistent and nonpersistent virtual desktops. In persistent desktop virtualizations, users can customize the desktop image by logging into the host server. Nonpersistent virtual desktops are available when a user logs out. Both types have advantages, such as better security and centralized desktop management.
The advantages of host virtualization are numerous. Because it runs on a central server, the VM exists as a single large file, which makes it easy to backup or migrate to different hardware. A host-based desktop virtualization solution also allows the VM to be restored to a previous state with the use of differencing files. A user can simply delete a checkpoint snapshot before proceeding with changes. In this way, they can easily rollback to the previous state of their system.